Title:Scalable Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Aryl C−H Phosphorylation Enabled by Anodic Oxidation Induced Reductive Elimination
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.. 2019, 58, 16770-16774
Authors:
Zheng-jian Wu, Feng Su, Weidong Lin, Jinshuai Song, Ting-bin Wen*, Hui-jun Zhang*, Hai-Chao Xu*
Abstract:
Transition metal catalyzed C−H phosphorylation remains an unsolved challenge. Reported methods are generally limited in scope and require stoichiometric silver salts as oxidants. Reported here is an electrochemically driven RhIII‐catalyzed aryl C−H phosphorylation reaction that proceeds through H2 evolution, obviating the need for stoichiometric metal oxidants. The method is compatible with a variety of aryl C−H and P−H coupling partners and particularly useful for synthesizing triarylphosphine oxides from diarylphosphine oxides, which are often difficult coupling partners for transition metal catalyzed C−H phosphorylation reactions. Experimental results suggest that the mechanism responsible for the C−P bond formation involves an oxidation‐induced reductive elimination process.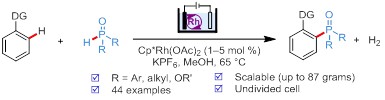
Published: 28August 2019
Full Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41929-019-0357-9