Title:Cooperative Stabilization of the [Pyridinium-CO2 -Co] Adduct on a Metal–Organic Layer Enhances Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 44, 17875-17883
Authors:
Ying Guo, Wenjie Shi, Huijuan Yang, Quanfeng He, Zhongming Zeng, Jin-yu Ye, Xinru He, Ruiyun Huang, Cheng Wang*,Wenbin Lin
Abstract:
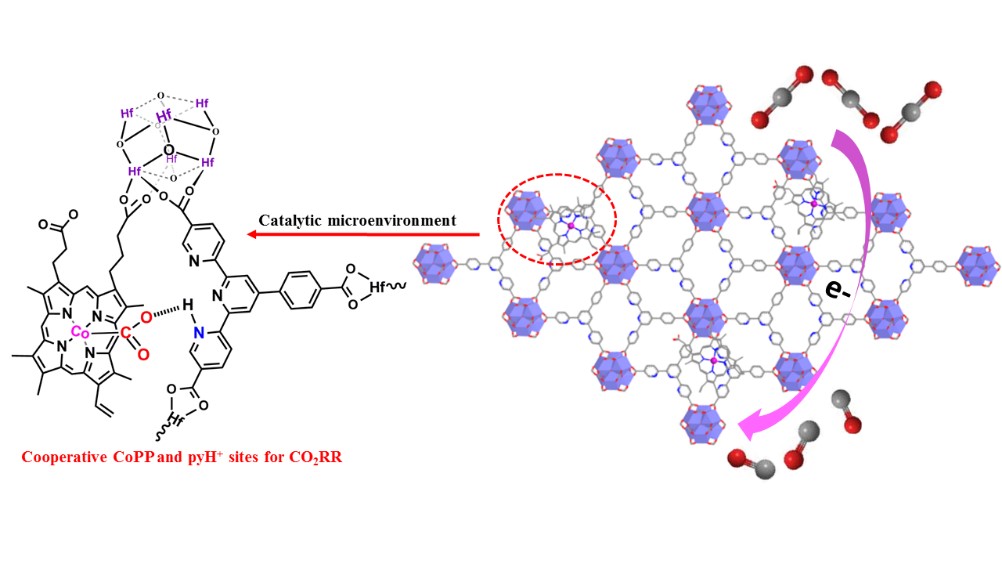
Pyridinium has been shown to be a cocatalyst for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 on metal and semiconductor electrodes, but its exact role has been difficult to elucidate. In this work, we create cooperative cobalt-protoporphyrin (CoPP) and pyridine/pyridinium (py/pyH+) catalytic sites on metal–organic layers (MOLs) for an electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). Constructed from [Hf6(μ3-O)4(μ3-OH)4(HCO2)6] secondary building units (SBUs) and terpyridine-based tricarboxylate ligands, the MOL was postsynthetically functionalized with CoPP via carboxylate exchange with formate capping groups. The CoPP group and the pyridinium (pyH+) moiety on the MOL coactivate CO2 by forming the [pyH+-–O2C-CoPP] adduct, which enhances the CO2RR and suppresses hydrogen evolution to afford a high CO/H2 selectivity of 11.8. Cooperative stabilization of the [pyH+-–O2C-CoPP] intermediate led to a catalytic current density of 1314 mA/mgCo for CO production at −0.86 VRHE, which corresponds to a turnover frequency of 0.4 s–1.
Published: 11October 2019
Full Link:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.9b09227