A Nanocomposite of Bi Clusters and Bi2O2CO3 Sheets for Highly Efficient Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to Formate
Authors: Li Lin, Xiaoyang He, Xia-Guang Zhang, Wenchao Ma, Biao Zhang, Diye Wei, Shunji Xie, Qinghong Zhang, Xiaodong Yi, Ye Wang*
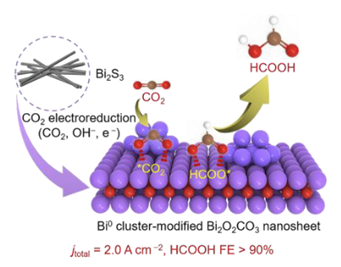
Abstract: As one of the most promising CO2 utilization routes, the renewable electricity-driven CO2 reduction to formic acid would contribute to establishing a carbon-neutral society. The current catalyst suffers from limited activity and stability under high selectivity and the ambiguous nature of active sites. Here, we report a powerful Bi2S3-derived catalyst that demonstrates a current density of 2.0 A cm-2 with a formate Faradaic efficiency of 93% at -0.95 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode. The energy conversion efficiency and single-pass yield of formate reach 80% and 67%, respectively, and the durability reaches 100 h at an industrial-relevant current density. Pure formic acid with a concentration of 3.5 mol L-1 has been produced continuously. Our operando spectroscopic and theoretical studies reveal the dynamic evolution of catalyst into a nanocomposite composed of Bi0 clusters and Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets and the pivotal role of Bi0−Bi2O2CO3 interface in CO2 activation and conversion.
Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202214959