[Advanced Materials] Prof. Jun Li published a paper entitled “Synergistically Enhanced Co-Adsorption of Reactant and Hydroxyl on Platinum-Modified Copper Oxide for High-Performance HMF Oxidation”
Title: Synergistically Enhanced Co-Adsorption of Reactant and Hydroxyl on Platinum-Modified Copper Oxide for High-Performance HMF Oxidation
Authors: Jiaran Li, Rongxing Qiu, Siwang Zhang, Li Peng*, Yangyang Dong, Yuan Jiang, Yin Li, Nan Fang, Jia Yu, Jin-Chao Dong, Haohui Zheng, Lingzhi Ding, Jinlong Wan, Isil Akpinar, Junhua Kuang, Gaofeng Chen, Jinyu Ye, Yong Sun, Lu Lin, Shisheng Zheng*, Shuliang Yang*, Jun Li*, Jian-Feng Li*
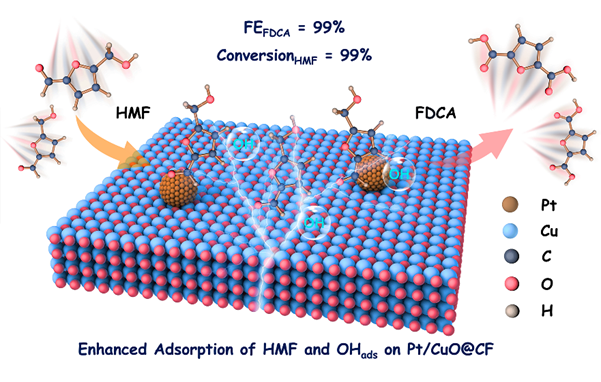
Abstract: Electrochemical oxidation of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) provides an environmentally friendly route for producing the sustainable polymer monomer 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). Thus, precisely adjusting the synergistic adsorption among key reactive species, such as HMF and OHads, on the carefully designed catalyst surface is essential for achieving satisfactory catalytic performance for HMF oxidation to FDCA as it is closely related to the adsorption strength and configuration of the reaction substrates. This kind of regulation will ultimately facilitate the improvement of HMF oxidation performance. In this work, Pt nanoparticles modified CuO nanowires (denoted as Pt/CuO@CF) are constructed for the selective electrooxidation of HMF to FDCA under alkaline conditions. The well-designed Pt/CuO@CF demonstrates highly impressive catalytic performance across a range of HMF concentrations, ranging from the commonly used concentrations to higher levels typically not explored (10, 25, 50, 75, and 100 mm) with high FEFDCA (all above 95%) and outstanding long-term stability (15 cycles). In situ experimental characterizations confirm that the designed heterogeneous interface between Pt and CuO enhances the enrichment of HMF and OHads species on the catalyst surface. Theoretical calculations reveal the anchored Pt nanoparticles reduce the adsorption barrier for HMF and OHads, thereby promoting the highly selective oxidation of HMF to FDCA.
Full-Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202417684