Title: Coulomb Field-Driven Desorption/Ionization by Femtosecond Laser for Mass Spectrometry Detection and Imaging
Authors: Heng Zhang, Jingkai Luo, Qi Zhang, Yizhu Xu, Zhibin Yin*, Wei Hang*
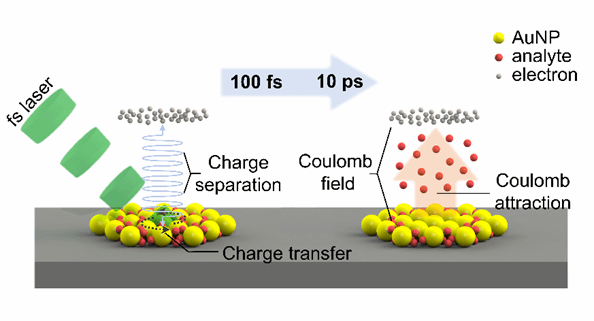
Abstract: Surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization (SALDI) offers promising prospects for mass spectrometry detection andimaging of small biomolecules, as it addresses most of the matrix-related issues encountered in conventional matrix-assisted laserdesorption/ionization (MALDI). Currently, nearly all of the fundamental aspects and applications of SALDI depend on nanosecond(ns) lasers, whereas few efforts have been made to integrate ultrafast femtosecond (fs) lasers with SALDI. Therefore, the intrinsicfundamental principle remains poorly understood. Herein, a novel surface-assisted femtosecond laser desorption/ionization massspectrometry (fs-SALDI-MS) platform was developed, which significantly reduces analyte fragmentation and preserves molecularintegrity. Spectral interferences from surface-assisted materials and alkali-metal adducts are absent in fs-SALDI mass spectra. Ionsurvival yields continuously increase with decreasing laser pulse widths from 5 ns to 600 fs, highlighting a gradual transition fromthermal to nonthermal effects. A lower absolute limit of detection down to ∼3 amol for representative antifungal and psychotropicdrugs and clearer visualization of ultratrace drug residues on latent fingerprints can be achieved, indicating that fs-SALDI results ingentler and more efficient detection/ionization processes than mainstream ns-SALDI. The biological applicability of this method wasfurther validated through 10 μm-spatial-resolution lipid imaging of mouse brain sections. In short, a novel Coulomb field-drivendesorption/ionization mechanism is proposed for fs-SALDI, opening new avenues for the development of emerging fs-SALDItechniques with superior analytical performance.
Full-Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c18652