Title: Unraveling CO-Tolerance Mechanism in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells via Operando Infrared Spectroscopy
Authors: Zhi-You Zhou*, Jia-Feng Du, Jin-Yu Ye, Chao Yang, Chun-Yu Qiu, Nan Fang, Yu-Cheng Wang, Shi-Gang Sun
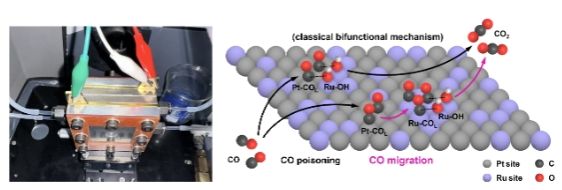
Abstract: CO poisoning remains a critical challenge for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Current studies of CO tolerance primarily focus on solid/liquid interfaces (in-situ conditions), which differ significantly from PEMFCs' solid/liquid/gas triple-phase interfaces (operando conditions) in microenvironment and mass transport. Herein, we developed an operando transmission infrared spectroscopy method that enables direct observation of CO tolerance mechanism on commercial PtRu/C catalysts in PEMFCs. Under in-situ conditions, hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) activity is governed by CO mass transfer, and is insensitive to the availability of active sites, while it is highly sensitive under operando conditions due to enhanced mass transfer, thereby aggravating CO poisoning effects. Notably, 76% of HOR activity can recover upon switching to pure H2. Based on CO band evolution, we proposed a new pathway beyond the traditional bifunctional mechanism of CO tolerance: CO migrates from Pt to Ru sites, undergoing oxidation at potentials as low as 0.01 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE).
Full-Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202503868