Title: A concurrently optimization of H and OH binding energies in atomically Ni anchored Ru/RuO2 nanosheet driving high CO-tolerant hydrogen oxidation catalysis
Authors: Liangbin Liu, Lujie Jin, Renjie Ren, Wei Yan, Nan Fang, Yujin Ji, Youyong Li, Lin Zhuang, Qingyu Kong, Zhiwei Hu, Qi Shao* & Xiaoqing Huang*
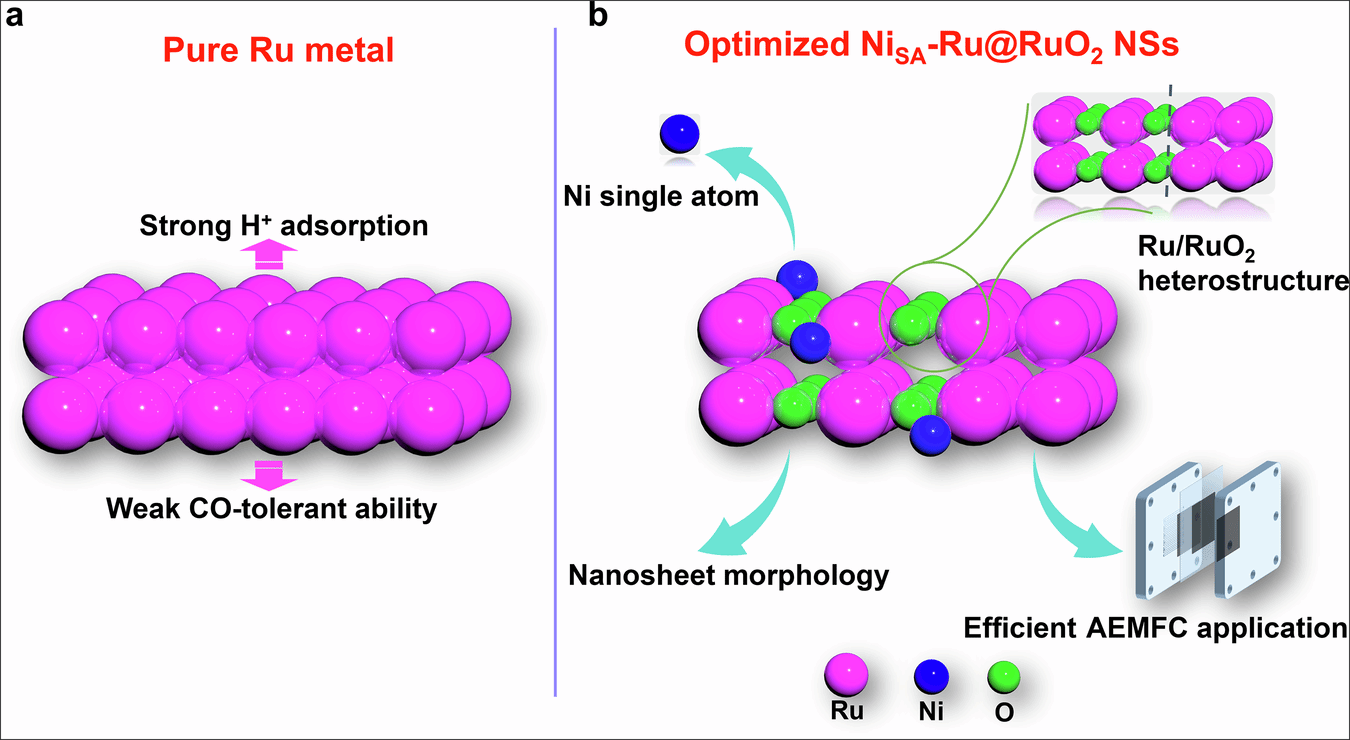
Abstract: The development of highly active and CO-tolerant hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) electrocatalysts is of great significance for alkaline exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs). Here, the designed atomically Ni anchored Ru/RuO2 heterostructure nanosheets (NiSA-Ru@RuO2 NSs/C) exhibit enhanced activity and stability for HOR in alkaline media. The optimized electrocatalyst delivers a high CO-tolerant durability with 92.3% retention in the 1000 ppm CO concentration after 5000 s test. Moreover, the anode catalyst NiSA-Ru@RuO2 NSs/C assembled AEMFCs output a peak power density (PPD) and specific PPD of 1.76 W cm−2 and 17.6 W mgPGM−1 under the H2/O2 condition and performed a long-term stability with negligible decay for 100 h at 0.5 A cm−2 for the AEMFCs. The relative mechanism studies reveal that the Ru/RuO2 heterostructure nanosheet and dispersed Ni single atoms have optimized the *H and *OH adsorption simultaneously and weaken the *CO adsorption. Our work may offer a significant guideline on the rational design of high-performance HOR electrocatalyst for energy-related applications.
Full-Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63998-8