Title: Tailored Electronic Metal–Support Interaction Boosts Hydrogen Release from Organic Carriers
Authors: Fan Luo, Zhiyao Liang, Wentong Jing, Yingjie Lai, Jiajun Huang, Xiongkai Tang, Lei Li, Zhe Yang, Ruixuan Qin*, Nanfeng Zheng*
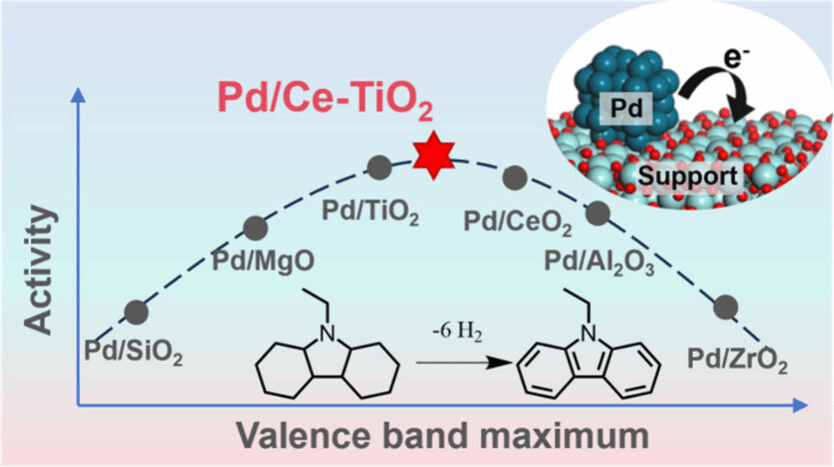
Abstract: The support plays a pivotal role in heterogeneous catalysis by not only providing stable binding sites for nanoparticles but also modulating their morphology and electronic properties. In this study, we systematically investigated the electronic effects on the catalytic dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole─a promising liquid organic hydrogen carrier─using well-defined palladium nanoparticles (Pd NPs) supported on various metal oxides. Our findings reveal that the catalytic behavior of Pd NPs is strongly influenced by charge transfer interactions, which are dictated by the energy gap between the Pd Fermi level and the valence band maximum of the support material. This interfacial electron transfer governs the electronic metal–support interaction, leading to a volcano-shaped correlation between the H2 production rate and the electronic state of Pd. Moreover, our study highlights that different stages of the dehydrogenation process require distinct electronic states. Leveraging these insights, we designed a high-performance catalyst comprising ultrafine Pd NPs supported on a binary metal oxide. The resulting Pd/Ce-TiO2 catalyst outperformed previously reported systems by facilitating stepwise dehydrogenation through a tandem mechanism.
Full-Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c12538